Probabilistic Face Embeddings Save
(ICCV 2019) Uncertainty-aware Face Representation and Recognition
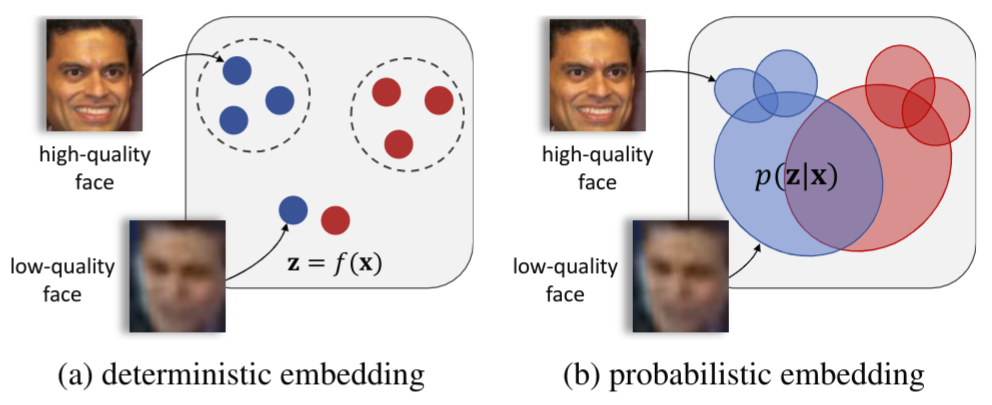
Probabilistic Face Embeddings
News: Our paper has been accepted to ICCV 2019.
This is a demo code of training and testing Probabilistic Face Embeddings using Tensorflow. Probabilistic Face Embeddging (PFE) is a method that converts conventional CNN-based face embeddings into probabilistic embeddings by calibrating each feature value with an uncertainty value. The representation of each face will be an Guassian distribution parametrized by (mu, sigma), where mu is the original embedding and sigma is the learned uncertainty. Experiments show that PFE could
- improve the performance of face recognition models by taking uncertainty into account.
- give more insight into the models' understanding of faces and more controll over potential risks.
 Compatability
Compatability
Currently this repo is compatible with Python 3 and Tensorflow r1.9.
 Update Notes
Update Notes
- 07/08/2019: Correct the CASIA file list.
- 30/04/2019: Upload more pre-trained models.
- 19/04/2019: Initial Upload.
 Citation
Citation
@article{shi2019PFE,
title = {Probabilistic Face Embeddings},
author = {Shi, Yichun and Jain, Anil K.},
booktitle = {arXiv:1904.09658},
year = {2019}
}
 Usage
Usage
Note: In this section, we assume that you are always in the directory $PROJECT_ROOT/
Preprocessing
In this demo, we will use CASIA-WebFace, LFW and IJB-A as examples for training and testing PFEs. In this section, we will align these datasets with the landmarks I pre-extracted.
- Download the original images of CASIA-WebFace dataset and align the images with the following command:
If you want to train the Ms-ArcFace model, you can download the dataset here and decode it using this code.python align/align_dataset.py data/ldmark_casia_mtcnncaffe.txt \ data/casia_mtcnncaffe_aligned \ --prefix /path/to/CASIA-Webface/images \ --transpose_input --image_size 96 112 - Download the original images of LFW dataset and align the images with the following command:
python align/align_dataset.py data/ldmark_lfw_mtcnncaffe.txt \ data/lfw_mtcnncaffe_aligned \ --prefix /path/to/LFW/images \ --transpose_input --image_size 96 112 - Download the IJB-A dataset and crop the faces with the following command:
To crop the images, you need to make sure that there are two folders under the given dataset folder:python align/crop_ijba.py proto/IJB-A/metadata.csv \ /path/to/IJB-A/images/ \ data/ijba_cropped/imgandframe. After cropping, align the images with the following command:python align/align_dataset.py data/ldmark_ijba_mtcnncaffe.txt \ data/ijba_mtcnncaffe_aligned \ --prefix data/ijba_cropped \ --transpose_input --image_size 96 112
Training
-
Before training, you need to prepare a base embedding network. To use the example base model, download zip file and unzip the files under
pretrained/sphere64_caisa_am/. -
The configuration files for training are saved under
config/folder, where you can define the training data, pre-trained model, network definition and other hyper-parameters. -
The uncertainty module that we are going to train is in
models/uncertainty_module.py. -
Use the following command to run the default training configuration for the example base model:
python train.py config/sphere64_casia.pyThe command will create an folder under
log/sphere64_casia_am_PFE/, which saves all the checkpoints and summaries. The model directory is named as the time you start training.
Testing
-
Single Image Comparison We use LFW dataset as an example for single image comparison. Make sure you have aligned LFW images using the previous commands. Then you can test it on the LFW dataset with the following command:
python evaluation/eval_lfw.py --model_dir /path/to/your/model/directory \ --dataset_path data/lfw_mtcnncaffe_aligned -
Template Fusion and Comparison We use IJB-A dataset as an example for template face comparison. Make sure you have aligned IJB-A images using the previous commands. Then you can test it on the IJB-A dataset with the following command:
python evaluation/eval_ijb.py --model_dir /path/to/your/model/directory \ --dataset_path data/ijba_mtcnncaffe_aligned -
Note that in the original paper, I used Matlab to normalize the images, but this demo uses pure python implementation. So the performance could be slightly different.
Visualization of Uncertainty
TODO
 Pre-trained Model
Pre-trained Model
64-CNN on CASIA-WebFace:
Base Mode: Google Drive
PFE: Google Drive
64-CNN on MS-ArcFace:
Base Mode: Google Drive
PFE: Google Drive
Note: In the paper we used a different version of Ms-Celeb-1M. According to the authors of ArcFace, this dataset (MS-ArcFace) has already been cleaned and has no overlap with the test data.
Test Results:
| Model | Method | LFW | IJB-A (FAR=0.1%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 64-CNN CASIA-WebFace | Baseline | 99.20 | 83.21 |
| 64-CNN CASIA-WebFace | PFE | 99.47 | 87.53 |
| 64-CNN Ms-ArcFace | Baseline | 99.72 | 91.93 |
| 64-CNN Ms-ArcFace | PFE | 99.83 | 94.82 |
(The PFE models and test results are obtained using exactly this demo code)
