Leaderj1001 RandWireNN Save
Implementing Randomly Wired Neural Networks for Image Recognition, Using CIFAR-10 dataset, CIFAR-100 dataset
Project README
Randomly Wired Neural Network
- Implement Exploring Randomly Wired Neural Networks for Image Recognition :)
Experiments
| Datasets | Model | Accuracy | Epoch | Training Time | Model Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIFAR-10 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=78 | 93.61% | 77 | 3h 50m | 4.75M |
| CIFAR-10 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=109 | 94.03% | 62 | 3h 50m | 8.93M |
| CIFAR-10 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=154 | 94.23% | 94 | 8h 40m | 17.31M |
| CIFAR-100 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=78 | 73.63% | 97 | 4h 46m | 4.87M |
| CIFAR-100 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=109 | 75.00% | 99 | 6h 9m | 9.04M |
| CIFAR-100 | RandWireNN(4, 0.75), c=154 | 75.42% | 99 | 9h 32m | 17.43M |
| IMAGENET | WORK IN PROGRESS | WORK IN PROGRESS |
Update (2019.05.06)
- Visualize weights
- Add directory of Drop Connection regularization RandWireNN
Update (2019.04.20)
- I added graphing functions for train accuracy, test accuracy, and train loss.
- I have added a part to report learning time and accuracy. Reporting of the above results can be seen in the reporting folder.
Todo
- Experiment with Imagenet dataset.
- To implement Optimzier like the paper.
Plot
CIFAR-10
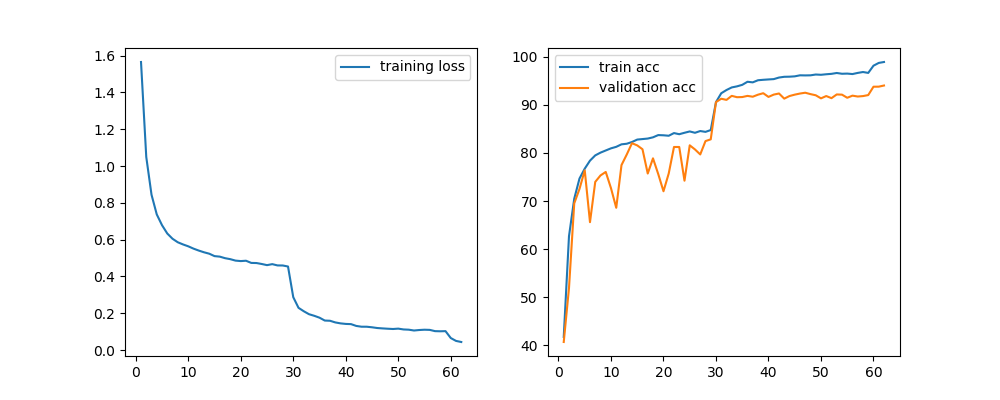
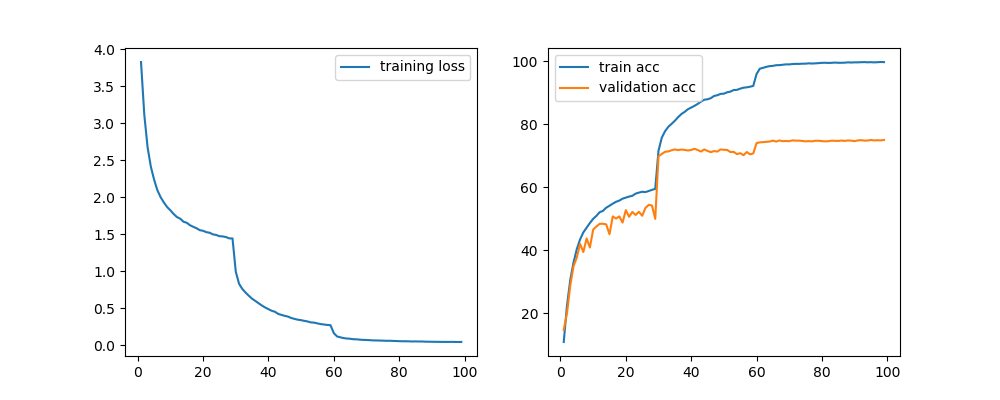
CIFAR-100
Visualize layer
- As each Epoch passes, we can see that the feature map is formed around the object.
Run
python main.py
- If you want to change hyper-parameters, you can check "python main.py --help"
Options:
-
--epochs(int) - number of epochs, (default: 100). -
--p(float) - graph probability, (default: 0.75). -
--c(int) - channel count for each node, (example: 78, 109, 154), (default: 78). -
--k(int) - each node is connected to k nearest neighbors in ring topology, (default: 4). -
--m(int) - number of edges to attach from a new node to existing nodes, (default: 5). -
--graph-mode(str) - kinds of random graph, (exampple: ER, WS, BA), (default: WS). -
--node-num(int) - number of graph node (default n=32). -
--learning-rate(float) - learning rate, (default: 1e-1). -
--model-mode(str) - which network you use, (example: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, SMALL_REGIME, REGULAR_REGIME), (default: CIFAR10). -
--batch-size(int) - batch size, (default: 100). -
--dataset-mode(str) - which dataset you use, (example: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, MNIST), (default: CIFAR10). -
--is-train(bool) - True if training, False if test. (default: True). -
--load-model(bool) - (default: False).
Test
python test.py
- Put the saved model file in the checkpoint folder and saved graph file in the saved_graph folder and type "python test.py".
- If you want to change hyper-parameters, you can check "python test.py --help"
- The model file currently in the checkpoint folder is a model with an accuracy of 92.70%.
Options:
-
--p(float) - graph probability, (default: 0.75). -
--c(int) - channel count for each node, (example: 78, 109, 154), (default: 78). -
--k(int) - each node is connected to k nearest neighbors in ring topology, (default: 4). -
--m(int) - number of edges to attach from a new node to existing nodes, (default: 5). -
--graph-mode(str) - kinds of random graph, (exampple: ER, WS, BA), (default: WS). -
--node-num(int) - number of graph node (default n=32). -
--model-mode(str) - which network you use, (example: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, SMALL_REGIME, REGULAR_REGIME), (default: CIFAR10). -
--batch-size(int) - batch size, (default: 100). -
--dataset-mode(str) - which dataset you use, (example: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, MNIST), (default: CIFAR10). -
--is-train(bool) - True if training, False if test. (default: False).
Reference
-
Exploring Randomly Wired Neural Networks for Image Recognition
- Author: Saining Xie Alexander Kirillov Ross Girshick Kaiming He(Facebook AI Research, FAIR)
- The paper is really awesome.
- Random Graph Generator Module(networkx)
- Visualize Network in Pytorch
- Must have Module, cairosvg
- Separable Convolution Code
- CIFAR benchmark
- CIFAR datasets
- IMAGENET datasets
- Really thank you :)
Methods
- Erdos-Renyi (ER) Graph, Watts-Strogatz (WS) Graph and Barabasi-Albert (BA) Graph are all available.
- If you want to visualize the network connection, you can follow the jupyter notebook in visualize_graph directory.
- Label smoothing.
- In CIFAR-10, The accuracy was 92.00%.
- But, CIFAR-100, I have seen improvements in CIFAR-100.
Version
- Windows 10, Pycharm community...
- Python 3.7
- Cuda 9.2
- Cudnn 7.1.4
- pytorch 1.0.1
- networkx 2.2
- torchviz 0.0.1
- graphviz 0.10.1
- tqdm 4.31.1
- conda install cairo(If you want to visualize the network, it is a required module.)
Network Image
- I have presented two graph visualizations. The ONNX module seems to be visualized more intuitively.
Small Network Image
- It is a picture of the sample small network in the visualize_graph directory.
- When I draw the contents of "Exploring Randomly Wired Neural Networks for Image Recognition" on the network, too many nodes are created. So I tried to draw a small network for visualization.
- Number of nodes: 7
- Graph parameters(probability P): 0.4
- Random seed: 12
- In_channels: 2
- Out_channels: 2
- The following figure is a simple example, and the basic RandWired NeuralNetwork Module is provided.
Example of Network

Open Source Agenda is not affiliated with "Leaderj1001 RandWireNN" Project. README Source: leaderj1001/RandWireNN
Stars
88
Open Issues
1
Last Commit
4 years ago
Repository
License



