Infrablocks Terraform Aws Ecs Cluster Save
Terraform module for building an ECS cluster in AWS
Terraform AWS ECS Cluster
A Terraform module for building an ECS Cluster in AWS.
The ECS cluster requires:
- An existing VPC
- Some existing subnets
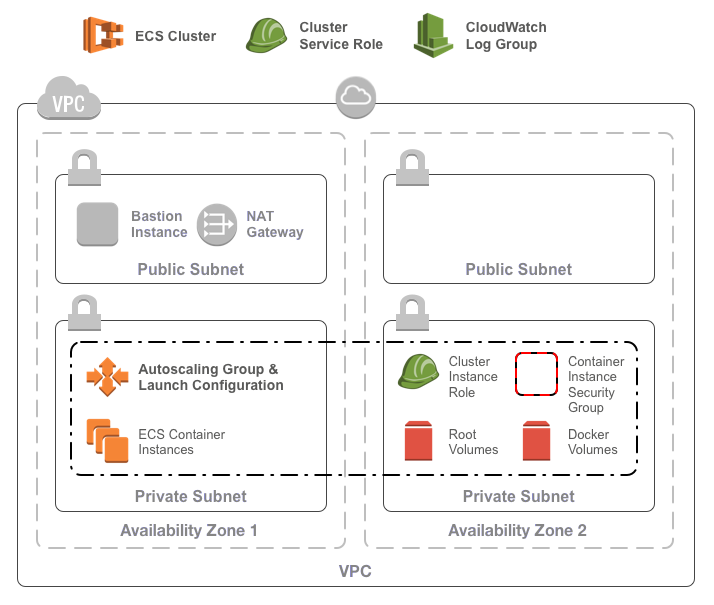
The ECS cluster consists of:
- A cluster in ECS
- A launch template and auto-scaling group for a cluster of ECS container instances
- An SSH key to connect to the ECS container instances
- A security group for the container instances optionally allowing:
- Outbound internet access for all containers
- Inbound TCP access on any port from the VPC network
- An IAM role and policy for the container instances allowing:
- ECS interactions
- ECR image pulls
- S3 object fetches
- Logging to cloudwatch
- An IAM role and policy for ECS services allowing:
- Elastic load balancer registration / deregistration
- EC2 describe actions and security group ingress rule creation
- A CloudWatch log group
Usage
To use the module, include something like the following in your Terraform configuration:
module "ecs_cluster" {
source = "infrablocks/ecs-cluster/aws"
version = "5.0.0"
region = "eu-west-2"
vpc_id = "vpc-fb7dc365"
subnet_ids = [
"subnet-eb32c271",
"subnet-64872d1f"
]
component = "important-component"
deployment_identifier = "production"
cluster_name = "services"
cluster_instance_ssh_public_key_path = "~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
cluster_instance_type = "t3.small"
cluster_minimum_size = 2
cluster_maximum_size = 10
cluster_desired_capacity = 4
}
As mentioned above, the ECS cluster deploys into an existing base network. Whilst the base network can be created using any mechanism you like, the AWS Base Networking module will create everything you need. See the docs for usage instructions.
See the Terraform registry entry for more details.
Inputs
| Name | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| region | The region into which to deploy the cluster | - | yes |
| vpc_id | The ID of the VPC into which to deploy the cluster | - | yes |
| subnet_ids | The IDs of the subnets for container instances | - | yes |
| component | The component this cluster will contain | - | yes |
| deployment_identifier | An identifier for this instantiation | - | yes |
| tags | A map of additional tags to add to all resources | - | no |
| cluster_name | The name of the cluster to create | default | yes |
| cluster_instance_ssh_public_key_path | The path to the public key to use for the container instances | - | yes |
| cluster_instance_type | The instance type of the container instances | t2.medium | yes |
| cluster_instance_root_block_device_size | The size in GB of the root block device on cluster instances | 30 | yes |
| cluster_instance_root_block_device_path | Path of the instance root block storage volume | /dev/xvda | yes |
| cluster_instance_root_block_device_type | The type of the root block device on cluster instances ('standard', 'gp2', or 'io1') | standard | yes |
| cluster_instance_user_data_template | The contents of a template for container instance user data | see user-data | no |
| cluster_instance_ami | AMI for the container instances | ECS optimised AMI | yes |
| cluster_instance_metadata_options | A map of metadata options for cluster instances. | - | no |
| cluster_instance_iam_policy_contents | The contents of the cluster instance IAM policy | see policies | no |
| cluster_service_iam_policy_contents | The contents of the cluster service IAM policy | see policies | no |
| cluster_minimum_size | The minimum size of the ECS cluster | 1 | yes |
| cluster_maximum_size | The maximum size of the ECS cluster | 10 | yes |
| cluster_desired_capacity | The desired capacity of the ECS cluster | 3 | yes |
| associate_public_ip_addresses | Whether or not to associate public IP addresses with ECS container instances | false | no |
| include_default_ingress_rule | Whether or not to include the default ingress rule on the ECS container instances security group | true | no |
| include_default_egress_rule | Whether or not to include the default egress rule on the ECS container instances security group | true | no |
| default_ingress_cidrs | The CIDRs allowed access to containers | ["10.0.0.0/8"] | if include_default_ingress_rule |
| default_egress_cidrs | The CIDRs accessible from containers | ["0.0.0.0/0"] | if include_default_egress_rule |
| security_groups | The list of security group IDs to associate with the cluster in addition to the default security group | [] | no |
| cluster_log_group_retention | The number of days logs will be retained in the CloudWatch log group of the cluster (0 = unlimited) | 0 | no |
| enable_detailed_monitoring | Enable detailed monitoring of EC2 instance(s) | true | no |
| enable_container_insights | Whether or not to enable container insights on the ECS cluster | false | no |
| protect_cluster_instances_from_scale_in | Whether or not to protect cluster instances in the autoscaling group from scale in | false | no |
| include_asg_capacity_provider | Whether or not to add the created ASG as a capacity provider for the ECS cluster | false | no |
| asg_capacity_provider_manage_termination_protection | Whether or not to allow ECS to manage termination protection for the ASG capacity provider | true | no |
| asg_capacity_provider_manage_scaling | Whether or not to allow ECS to manage scaling for the ASG capacity provider | true | no |
| asg_capacity_provider_minimum_scaling_step_size | The minimum scaling step size for ECS managed scaling of the ASG capacity provider | 1 | no |
| asg_capacity_provider_maximum_scaling_step_size | The maximum scaling step size for ECS managed scaling of the ASG capacity provider | 1000 | no |
| asg_capacity_provider_target_capacity | The target capacity, as a percentage from 1 to 100, for the ASG capacity provider | 100 | no |
| cluster_instance_enable_ebs_volume_encryption | Determines whether encryption is enabled on the EBS volume | true | no |
| cluster_instance_ebs_volume_kms_key_id | KMS key to use for encryption of the EBS volume when enabled | alias/aws/ebs | no |
Notes:
- By default, the latest available Amazon Linux 2 AMI is used.
- For Amazon Linux 1 AMIs use version <= 0.6.0 of this module for terraform 0.11 or version = 1.0.0 for terraform 0.12.
- When a specific AMI is provided via
cluster_instance_ami, only the root block device can be customised, using thecluster_instance_root_block_device_sizeandcluster_instance_root_block_device_typevariables. - The user data template will get the cluster name as
cluster_name. If none is supplied, a default will be used.
Outputs
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cluster_id | The ID of the created ECS cluster |
| cluster_name | The name of the created ECS cluster |
| cluster_arn | The ARN of the created ECS cluster |
| autoscaling_group_name | The name of the autoscaling group for the ECS container instances |
| launch_template_name | The name of the launch template for the ECS container instances |
| launch_template_id | The ID of the launch template for the ECS container instances |
| security_group_id | The ID of the default security group associated with the ECS container instances |
| instance_role_arn | The ARN of the container instance role |
| instance_role_id | The ID of the container instance role |
| instance_policy_arn | The ARN of the container instance policy |
| instance_policy_id | The ID of the container instance policy |
| service_role_arn | The ARN of the ECS service role |
| service_role_id | The ID of the ECS service role |
| service_policy_arn | The ARN of the ECS service policy |
| service_policy_id | The ID of the ECS service policy |
| log_group | The name of the default log group for the cluster |
Compatibility
This module is compatible with Terraform versions greater than or equal to Terraform 1.0.
Required Permissions
- iam:GetPolicy
- iam:GetPolicyVersion
- iam:ListPolicyVersions
- iam:ListEntitiesForPolicy
- iam:CreatePolicy
- iam:DeletePolicy
- iam:GetRole
- iam:PassRole
- iam:CreateRole
- iam:DeleteRole
- iam:ListRolePolicies
- iam:AttachRolePolicy
- iam:DetachRolePolicy
- iam:GetInstanceProfile
- iam:CreateInstanceProfile
- iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole
- iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile
- iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile
- iam:DeleteInstanceProfile
- ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups
- ec2:CreateSecurityGroup
- ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup
- ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress
- ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress
- ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress
- ec2:ImportKeyPair
- ec2:DescribeKeyPairs
- ec2:DeleteKeyPair
- ec2:CreateTags
- ec2:DescribeImages
- ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces
- ecs:DescribeClusters
- ecs:CreateCluster
- ecs:DeleteCluster
- autoscaling:DescribeLaunchConfigurations
- autoscaling:CreateLaunchConfiguration
- autoscaling:DeleteLaunchConfiguration
- autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities
- autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups
- autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup
- autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup
- autoscaling:DeleteAutoScalingGroup
- logs:CreateLogGroup
- logs:DescribeLogGroups
- logs:ListTagsLogGroup
- logs:DeleteLogGroup
Development
Machine Requirements
In order for the build to run correctly, a few tools will need to be installed on your development machine:
- Ruby (3.1)
- Bundler
- git
- git-crypt
- gnupg
- direnv
- aws-vault
Mac OS X Setup
Installing the required tools is best managed by homebrew.
To install homebrew:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
Then, to install the required tools:
# ruby
brew install rbenv
brew install ruby-build
echo 'eval "$(rbenv init - bash)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'eval "$(rbenv init - zsh)"' >> ~/.zshrc
eval "$(rbenv init -)"
rbenv install 3.1.1
rbenv rehash
rbenv local 3.1.1
gem install bundler
# git, git-crypt, gnupg
brew install git
brew install git-crypt
brew install gnupg
# aws-vault
brew cask install
# direnv
brew install direnv
echo "$(direnv hook bash)" >> ~/.bash_profile
echo "$(direnv hook zsh)" >> ~/.zshrc
eval "$(direnv hook $SHELL)"
direnv allow <repository-directory>
Running the build
Running the build requires an AWS account and AWS credentials. You are free to configure credentials however you like as long as an access key ID and secret access key are available. These instructions utilise aws-vault which makes credential management easy and secure.
To provision module infrastructure, run tests and then destroy that infrastructure, execute:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go
To provision the module prerequisites:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:prerequisites:provision[<deployment_identifier>]
To provision the module contents:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:root:provision[<deployment_identifier>]
To destroy the module contents:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:root:destroy[<deployment_identifier>]
To destroy the module prerequisites:
aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go deployment:prerequisites:destroy[<deployment_identifier>]
Configuration parameters can be overridden via environment variables:
DEPLOYMENT_IDENTIFIER=testing aws-vault exec <profile> -- ./go
When a deployment identifier is provided via an environment variable, infrastructure will not be destroyed at the end of test execution. This can be useful during development to avoid lengthy provision and destroy cycles.
Common Tasks
Generating an SSH key pair
To generate an SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 4096 -C [email protected] -N '' -f config/secrets/keys/bastion/ssh
Generating a self-signed certificate
To generate a self signed certificate:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365
To decrypt the resulting key:
openssl rsa -in key.pem -out ssl.key
Managing CircleCI keys
To encrypt a GPG key for use by CircleCI:
openssl aes-256-cbc \
-e \
-md sha1 \
-in ./config/secrets/ci/gpg.private \
-out ./.circleci/gpg.private.enc \
-k "<passphrase>"
To check decryption is working correctly:
openssl aes-256-cbc \
-d \
-md sha1 \
-in ./.circleci/gpg.private.enc \
-k "<passphrase>"
Contributing
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/infrablocks/terraform-aws-assumable-roles-policy. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct.
License
The library is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.
