Earley Parser Js Save
Tiny JavaScript implementation of context-free languages parser - Earley parser (including generation of the parsing-forest).
earley-parser-js
Tiny JavaScript implementation of context-free languages parser - Earley parser
Table of contents
-
General information about Earley parsing algorithm
-
Online demo
2.1 Parser of the tiny subset of German grammar
2.2 Parser of the tiny subset of English grammar
2.3 Parser of arithmetic expressions
-
Quick start
3.1 Grammar with hardcoded terminal symbols
3.2 Customizing logic of tokens classification into terminal symbols
3.3 Traversing parsed trees (parsing-forest)
3.4 Parsing tiny subset of English language grammar
- Used Tools and Libraries
- This library is used by...
General information
The Earley parser is an algorithm for parsing strings that belong to a given context-free language (the algorithm, named after its inventor, Jay Earley).
This algorithm is appealing because it can parse all context-free languages, unlike LR parsers and LL parsers, which are more typically used in compilers but which can only handle restricted classes of languages.
Complexity of Earley parsing algorithm (in terms of n - the length of the parsed string):
- O(n3) - cubic time in the general case
- O(n2) - quadratic time for unambiguous grammars
- O(n) - linear time for almost all LR(k) grammars
Earley parser performs particularly well when the rules are written left-recursively.
Online demo
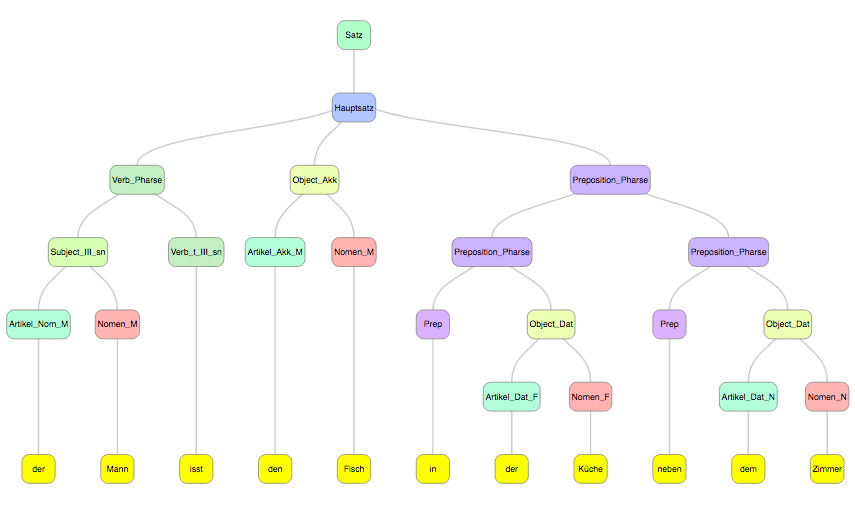
Parser of the tiny subset of German grammar
Parser of the tiny subset of German grammar: http://lagodiuk.github.io/nlp/deutsch.html
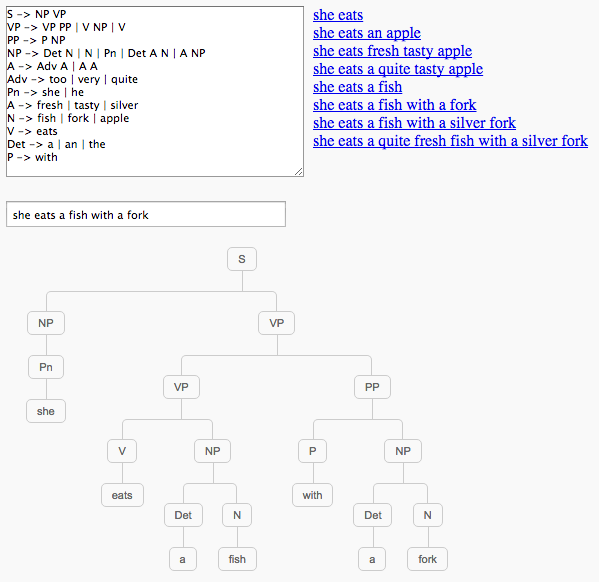
Parser of the tiny subset of English grammar
Parser of a tiny subset of English grammar: https://jsfiddle.net/2mb3w9c1/4/embedded/result/
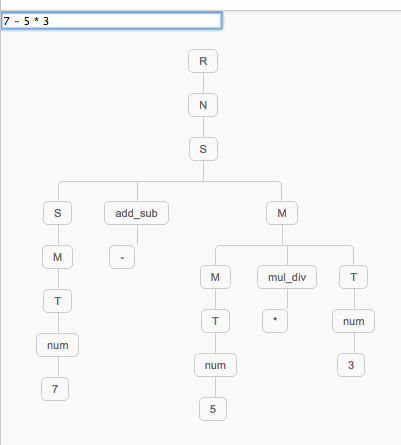
Parser of arithmetic expressions
Parser of arithmetic expressions: https://jsfiddle.net/vsf982m9/embedded/result/
var grammar = new tinynlp.Grammar([
'R -> N',
'S -> S add_sub M | M',
'M -> M mul_div T | T',
'N -> S lt_gt S | S',
'T -> num | ( S )',
]);
grammar.terminalSymbols = function(token) {
if ('<' === token || '>' === token) return ['lt_gt'];
if ('+' === token || '-' === token) return ['add_sub'];
if ('*' === token || '/' === token) return ['mul_div'];
if ('(' === token) return ['('];
if (')' === token) return [')'];
// Otherwise - token considered as a number:
return ['num'];
}
Usage
Attach to your project - single file with implementation of Earley algorithm: https://rawgithub.com/lagodiuk/earley-parser-js/master/earley-oop.min.js
Grammar with hardcoded terminal symbols
// Define grammar
var grammar = new tinynlp.Grammar([
// Define grammar production rules
'R -> S',
'S -> S add_sub M | M | num',
'M -> M mul_div T | T | num',
'T -> num',
// Define terminal symbols
'num -> 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0',
'add_sub -> + | -',
'mul_div -> * | /'
]);
// You have to tokenize input by yourself!
// Creating array of tokens
var tokens = '2 + 3 * 4'.split(' ');
// Parsing
var rootRule = 'R';
var chart = tinynlp.parse(tokens, grammar, rootRule);
// Get array with all parsed trees
// In case of ambiguous grammar - there might be more than 1 parsing tree
var trees = chart.getFinishedRoot(rootRule).traverse();
// Iterate over all parsed trees and display them on HTML page
for (var i in trees) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(trees[i]))
}
Customizing logic of tokens classification into terminal symbols
Potentially, this approach allows to extend parser with custom classifier of tokens - into terminal symbols (e.g. recognize terminal symbols using Regular expressions or more sophisticated classifiers):
var grammar = new tinynlp.Grammar([
'R -> S',
'S -> S add_sub M | M | num',
'M -> M mul_div T | T | num',
'T -> num',
]);
// Define function, which will classify tokens into terminal types
grammar.terminalSymbols = function( token ) {
// Actually, this method might be customized
// to use some more sophisticated classification mechanisms
if( '+' === token || '-' === token ) return ['add_sub'];
if( '*' === token || '/' === token ) return ['mul_div'];
if( token.match(/^\d+$/) ) return ['num'];
// It is also possible that classifier returns
// more than one terminal symbol, e.g.: ['term1', 'term2']
// Otherwise:
throw new Error("Can't recognize token: " + token);
}
// You have to tokenize input by yourself!
// Creating array of tokens
var tokens = '2 + 3 * 4'.split(' ');
// Parsing
var rootRule = 'R';
var chart = tinynlp.parse(tokens, grammar, rootRule);
// Get array with all parsed trees
// In case of ambiguous grammar - there might be more than 1 parsing tree
var trees = chart.getFinishedRoot(rootRule).traverse();
// Iterate over all parsed trees and display them on HTML page
for (var i in trees) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(trees[i]))
}
Traversing parsed trees
Following snippet shows how to transform parsed trees into nested HTML lists:
function toNestedList(tree) {
if (!tree.subtrees || tree.subtrees.length == 0) {
return '<li>' + tree.root + '</li>';
}
var builder = [];
builder.push('<li>');
builder.push(tree.root);
builder.push('<ul>')
for (var i in tree.subtrees) {
builder.push(toNestedList(tree.subtrees[i]))
}
builder.push('</ul>')
builder.push('</li>')
return builder.join('');
}
Example of usage:
// Iterate over all parsed trees and display them on HTML page
for (var i in trees) {
htmlRepresentstion = '<ul>' + toNestedList(trees[i]) + '</ul>'
// embed htmlRepresentstion into HTML page
}
Parsing tiny subset of English language grammar
Grammar taken from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CYK_algorithm#Example
var grammar = new tinynlp.Grammar([
'S -> NP VP',
'VP -> VP PP | V NP | V',
'PP -> P NP',
'NP -> Det N | N'
]);
grammar.terminalSymbols = function(token) {
if(token == 'eats') return ['V'];
if(token == 'fish') return ['N'];
if(token == 'fork') return ['N'];
if(token == 'she') return ['N'];
if(token == 'a') return ['Det'];
if(token == 'with') return ['P'];
// otherwise:
return [];
}
// Tokenizing sentence
var tokens = 'she eats a fish with a fork'.split(' ');
// Parsing
var rootRule = 'S';
var chart = tinynlp.parse(tokens, grammar, rootRule);
// Get array with all parsed trees
// In case of ambiguous grammar - there might be more than 1 parsing tree
var trees = chart.getFinishedRoot(rootRule).traverse();
for (var i in trees) {
// visit each parse tree
}
Used Tools and Libraries
Implementation of the Earley Parser is self-sufficient (https://github.com/lagodiuk/earley-parser-js/blob/master/earley-oop.js).
However, for producing of the minimized variant of library was used the Google Closure Compiler Service.
Additionally, some of the demo examples are using:
Some of the demo examples are currently hosted on https://jsfiddle.net/
This library is used by...
- The web site of the book "Formale Sprachen, abstrakte Automaten und Compiler: Lehr- und Arbeitsbuch für Grundstudium und Fortbildung" (by Christian Wagenknecht (Autor), Michael Hielscher (Mitwirkende)): https://flaci.com/home/ The library is used by this web site for creation of the browser environment, where users can experiment with different Context Free Grammars (define grammars and produce the parsing trees on the fly)
