Dotnet Onion Architecture Save
.Net onion/clean architecture sample
Onion Architecture / Clean Architecture

- Onion architecture can solve problem of separation of concern and tightly coupled components from N-layered architecture.
- All layers are depended on inner layer.
- The core of the application is the domain layer.
- Provide more testability than N-layered architecture.
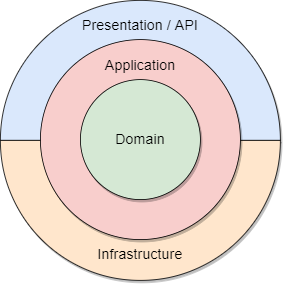
Layers
Domain Layer:
This layer does not depend on any other layer. This layer contains entities, enums, specifications etc.
Add repository and unit of work contracts in this layer.
Application Layer:
This layer contains business logic, services, service interfaces, request and response models.
Third party service interfaces are also defined in this layer.
This layer depends on domain layer.
Infrastructure Layer:
This layer contains database related logic (Repositories and DbContext), and third party library implementation (like logger and email service).
This implementation is based on domain and application layer.
Presentation Layer:
This layer contains Webapi or UI.
Domain model
Domain model are of 2 types
-
Domain entity (data only)
- This model contains only fields
- This is an anti pattern used widely. Read blog from Martin Fowler (here)
-
Domain model (data + behaviour)
- This model has fields and behaviours. Fields can be modify only within behaviours.
- Follow Aggregate pattern with Aggregate root, Value object, Entity, Bounded context, Ubiqutous language
Validations in Domain driven design:
There are 2 types of validations in DDD:
-
Model Field validations
- Properties having valid length
- required field validations
- regex
Model validations can be validated in Application layer or Domain layer.
- Use DataAnnotation (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.componentmodel.dataannotations?view=net-7.0)
- Use Guard pattern (https://github.com/NilavPatel/Guard-Pattern)
- mostly used when you have single source of truth (validations in aggregate pattern)
- Use fluent validations pattern (https://docs.fluentvalidation.net/en/latest/aspnet.html)
- Used when validating models instead of single properties like request models, commands
-
Business validations
- Balance should be more than Withdraw amount
- User should be active
- User name should not be exist
Business validations can be validated in Applciation layer or Domain layer.
Business validations have two types:
- Validations in same domain model
- Balance should be more than Withdraw amount
- User should be active
- Validations against other domain models
- User name should not be already exist
For Aggregate pattern add both types of validations inside domain layer.
Problem occurs when validating domain model against other domain models.
- In this case use Func<> methods to pass validations to domain model from Application layer.
And run this Func<> from domain models.
public WithdrawMoney(double amount, Func<string, bool> isBankAccountActive){
if(!isBankAccountActive(BankAccountNumber)){
throw new DomainValidationException("Bank account is not in active state");
}
}
- Otherwise pass domain model of other type as parameter and then validate.
public WithdrawMoney(double amount, BankAccount bankAccount){
if(bankAccount.Status != Active){
throw new DomainValidationException("Bank account is not in active state");
}
}
For more details read
Technologies Used:
- .Net 8
- Rest API
- Entity Framework
- NLog
- Swagger
- Xunit
- Moq
- Generic Repository Pattern
- Specification pattern
