Docker Redis Haproxy Cluster Save
A Redis Replication Cluster accessible through HAProxy running across a Docker Composed-Swarm with Supervisor and Sentinel
A Redis Cluster accessible via HAProxy and configured for Replication using Sentinel and Supervisor hosted in a Docker Composed-Swarm
Overview
This repository will start a distributed 3-node replication cluster using Redis, Sentinel and Supervisor using Docker Swarm and Compose for high availability. Access to the Redis cluster is done through HAProxy on TCP Port 9000. HAProxy is configured to discover and stay connected to the Redis Master instance, which means Redis Clients will only need to reconnect while HAProxy handles the discovery of the newly elected master instance.
Running Three Replication Clusters on a single AWS EC2 Instance
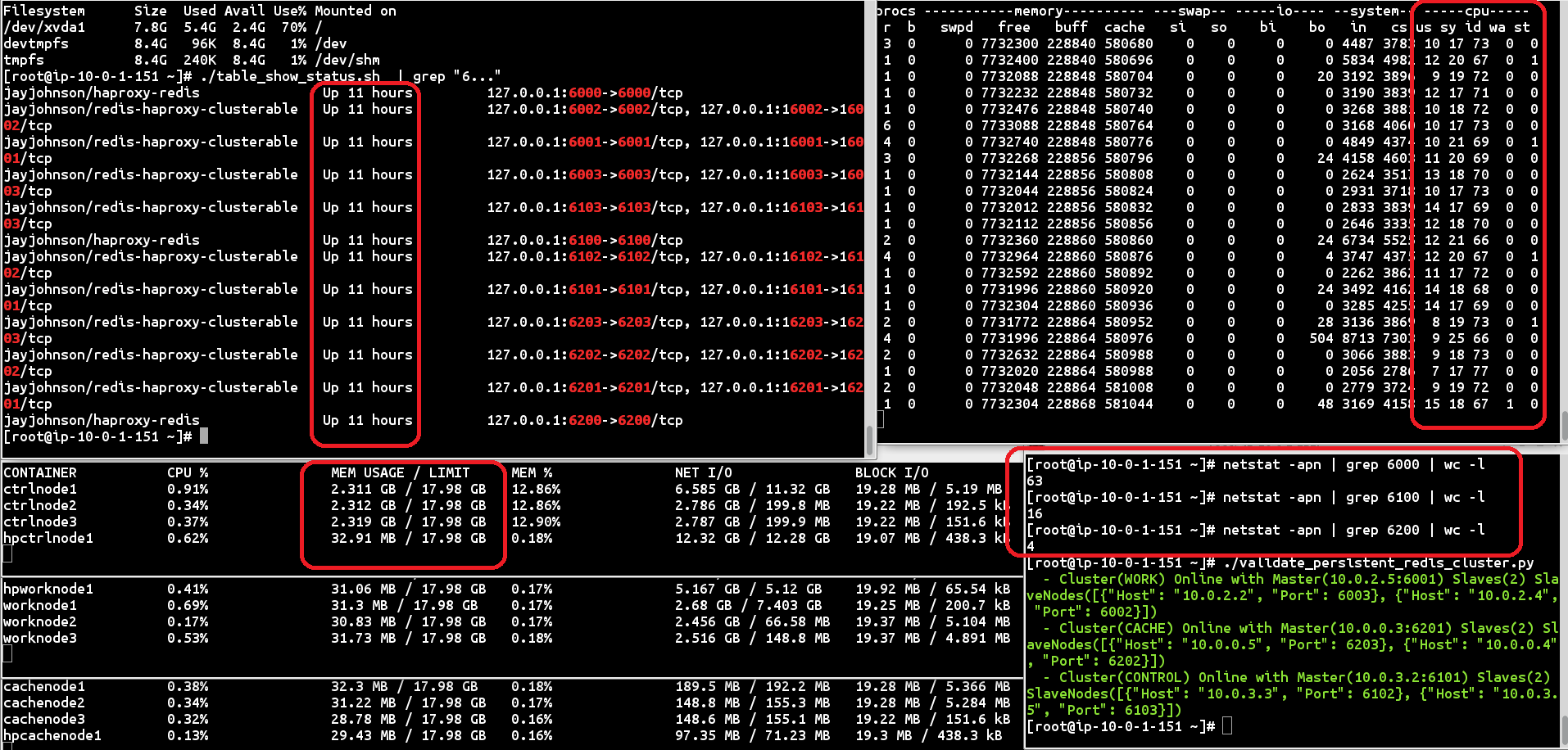
I was curious how many Redis replication clusters I could put on one EC2 host, so I built three docker-compose.yml files with unique ports for ensuring no overlap across containers or overlay networks. Then I started testing the caching performance and replication across the cluster. I used an EC2 m2.xlarge and started all three replication clusters running inside a Docker Swarm. At the time of the screenshot, the 3 clusters have been up for 11 hours, the host is mostly idle (around 70%), there is around 2.31 GB cached and replicated across the Control cluster (ctrlnode1, ctrlnode2, ctrlnode3), and there are 63 persistent connections to the Control cluster. One point to note is that HAProxy is terminating idle Redis connections. This means I had to use the Retry Connection Support for all my Redis clients to handle and HAProxy disconnection event for idle/outages/failures/something-bad.
HA Publisher-Subscriber Message Testing
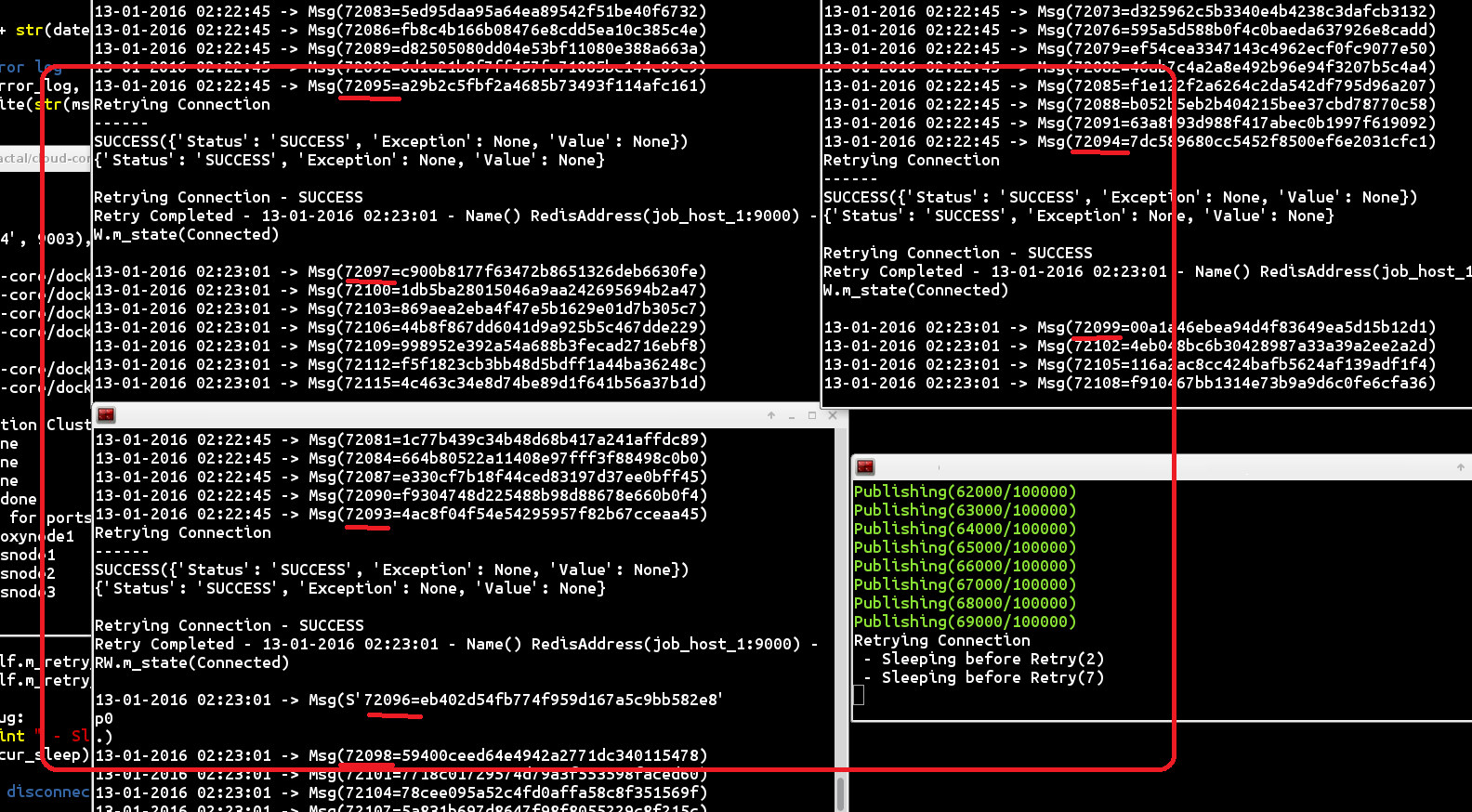
Here is a sample screenshot from a High Availability message simulation I used to validate this build. This simulation was running a single publisher instance that did a for-loop publishing 100,000 messages by building the buffer before writing to Redis. There were 3 subscribers reading messages in a round-robin sharing method and dequeueing messages sent from the publisher. While this was in action, I manually ran docker stop redisnode1 (or other nodes) to see how the replication cluster handled a critical failure. During testing, I was unable to see any message loss and the publisher and subscribers were automatically reconnected back to the new Redis Master instance once HAProxy discovered the new Master instance using the Redis Sentinel API.
Technical Details
There are 3 Redis instances listening on ports: 9001-9003. There can be only 1 master Redis node at a time and the other 2 nodes are set up for fault-tolerant replication with Sentinel and Supervisor. The goal of this replication cluster is to reduce message and data loss even when the master Redis node crashes. When the master node crashes Sentinel will host a leader election and another node will become the new master by winning the election. Supervisor runs in each container and will automatically attempt to restart any stopped Redis instance. Sentinel is paired up with each Redis server and listens on ports 19001-19003 (Redis Server Port + 10000). HAProxy listens on TCP Port 9000 and will always be connected to the Redis Master instance. If the container stays up while the Redis instance crashes, then Supervisor will restart the process. HAProxy is configured to restart using Supervisor as well. Additionally each container is setup for socket recycling, and logrotation on a cronjob.
How to Install
- Make sure Swarm is installed
docker-redis-haproxy-cluster $ sudo ./_install_docker_services.sh
- Restart the local consul, docker daemon, swarm manager, and swarm join
docker-redis-haproxy-cluster $ sudo ./boot_local_docker_services.sh
- Point to the Docker Swarm
Please set the terminal environment to use the running Docker Swarm
$ export DOCKER_HOST=localhost:4000
$ env | grep DOCKER
DOCKER_HOST=localhost:4000
$
- Confirm the Docker Swarm Membership
Running the swarm locally you should see only 1 node with something similar:
$ docker info
Containers: 0
Images: 0
Role: primary
Strategy: spread
Filters: health, port, dependency, affinity, constraint
Nodes: 1
localhost.localdomain: localhost:2375
└ Containers: 0
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 2
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 4.053 GiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.7-200.fc22.x86_64, operatingsystem=Fedora 22 (Twenty Two), storagedriver=devicemapper
CPUs: 2
Total Memory: 4.053 GiB
Name: localhost.localdomain
$
Start the Redis Replication Cluster
Assuming consul, docker daemon, swarm manager, and swarm join are running with something similar to:
$ ps auwwx | grep consul | grep -v grep
root 29447 0.4 0.4 34110388 19204 pts/4 Sl 19:39 0:14 consul agent -server -data-dir=/tmp/consul -bind=0.0.0.0 -bootstrap-expect 1
root 31650 12.9 1.2 1329604 51208 pts/4 Sl 20:00 3:42 /usr/local/bin/docker daemon -H localhost:2375 --cluster-advertise 0.0.0.0:2375 --cluster-store consul://localhost:8500/developmentswarm
root 31738 0.0 0.5 488084 20512 pts/1 Sl 20:02 0:01 /usr/local/bin/swarm manage -H tcp://localhost:4000 --advertise localhost:4000 consul://localhost:8500/developmentswarm
root 31749 0.0 0.3 128416 14304 pts/1 Sl 20:02 0:00 /usr/local/bin/swarm join --addr=localhost:2375 consul://localhost:8500/developmentswarm
$
- Make sure no other Redis nodes are running
$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
$
- Start the Redis Cluster
docker-redis-haproxy-cluster $ ./start_cluster.sh
Starting the Redis Replication Cluster with HAProxy on Docker Swarm
Creating haproxynode1
Creating redisnode1
Creating redisnode3
Creating redisnode2
Done
docker-redis-haproxy-cluster $
- Confirm the Containers are running
$ docker ps
b4d2f27a9af4 jayjohnson/redis-haproxy-clusterable "/bin/sh -c '. /bin/s" 30 seconds ago Up 28 seconds 127.0.0.1:9002->9002/tcp, 6379/tcp, 127.0.0.1:19002->19002/tcp localhost.localdomain/redisnode2
d3b6d9b1b062 jayjohnson/redis-haproxy-clusterable "/bin/sh -c '. /bin/s" 31 seconds ago Up 29 seconds 127.0.0.1:9003->9003/tcp, 6379/tcp, 127.0.0.1:19003->19003/tcp localhost.localdomain/redisnode3
dcd85d621fbc jayjohnson/redis-haproxy-clusterable "/bin/sh -c '. /bin/s" 31 seconds ago Up 30 seconds 127.0.0.1:9001->9001/tcp, 127.0.0.1:19001->19001/tcp, 6379/tcp localhost.localdomain/redisnode1
3f8b264ccb01 jayjohnson/haproxy-redis "/bin/sh -c '. /bin/s" 32 seconds ago Up 31 seconds 127.0.0.1:9000->9000/tcp localhost.localdomain/haproxynode1
$
Find the Redis Cluster Master Node using the Command Line Tool or Script
$ redis-cli -p 19001 sentinel get-master-addr-by-name redis-cluster
1) "10.0.0.3"
2) "9001"
$
$ ./tests/get_cluster_master.sh
1) "10.0.0.3"
2) "9001"
$
$ ./tests/cst.py
Master(('10.0.0.3', 9001))
Slaves(2) Nodes([('10.0.0.5', 9002), ('10.0.0.4', 9003)])
$
Integration with your Clients and Testing Simulated Failovers
The tests directory holds scripts to stop/start docker containers, publish messages, read messages as a subscriber, and print the cluster status all through the HAProxy interface. Here you can experiment with how your Redis Client(s) handle failover and disconnections at the HAProxy layer.
$ tree tests/
tests/
├── cst.py
├── get_cluster_master.sh
├── __init__.py
├── publish_messages.py
├── redis_wrapper.py
├── start_node_1.sh
├── start_node_2.sh
├── start_node_3.sh
├── stop_node_1.sh
├── stop_node_2.sh
├── stop_node_3.sh
└── subscribe_and_read_messages.py
$
Stop the Redis Cluster
$ ./stop_cluster.sh
Stopping the Redis Replication Cluster with HAProxy on Docker Swarm
Stopping redisnode2 ...
Stopping redisnode3 ...
Stopping redisnode1 ...
Stopping haproxynode1 ...
$
License
This is free to use under the MIT LICENSE.
Enjoy.
