BatchASM Save
BatchASM - primitive virtual machine (high level assembly language) for executing instructions in programming language environment Windows Batch.

About BatchASM
Introduction
BatchASM - primitive virtual machine for executing instructions in programming language environment Windows Batch. The virtual machine interpreter module is VM.CMD.
In the examples, call vm ... is used as the virtual machine initializer, which implies the use of the VM.CMD module with the specified input data.
Data stack view
The virtual machine has a built-in stack management system data, which is a set of objects, each of which is named in the format "stack.N", where "N" - number of the element on the stack. The stack is designed to store values and is managed manually. The numbering of stack elements starts from one. The numbering of stack elements starts with the value.
Opcodes for working with the data stack
-
push: Adds a value to the top of the stack. New value creates object "stack.N", where "N" - unique number.
-
clr: Clears all stack elements and frees memory.
-
push.ref: Copies a value from one object (or stack address) to another or stores it in memory under the specified name.
call vm push "Test!" &:: Data to be retained after clearing the stack call vm push.ref tmp.1 stack.1 &:: Storing the value of stack.1 into memory as tmp.1 call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents call vm push.ref stack.1 tmp.1 &:: Return value for stack.1 call vm push.clr tmp.1 &:: Removing tmp.1 from memory call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
push.mov: Moves a value from one object (or stack address) to another or stores it in memory under a specified name, first clearing the object (or stack address) from which the value is transferred. Makes it possible to simplify the use of
push.refandpush.clrby reducing it to one command.call vm push "Test!" &:: Data to be retained after clearing the stack call vm push.ref tmp.1 stack.1 &:: Storing the value of stack.1 into memory as tmp.1 call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents call vm push.mov stack.1 tmp.1 &:: Return value for stack.1 call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
push.clr: Clears the specified stack object or value.
call vm push.clr stack.3 &:: Clears the contents of the third stack element call vm push.clr tmp.1 &:: Clears the contents of the tmp.1 object
Mathematical operations
The virtual machine supports four basic mathematical operations. Each of them returns the result in stack.1:
-
add: Adding values
stack.1andstack.2 -
sub: Subtracting a value
stack.2fromstack.1 -
mul: Multiplying values
stack.1andstack.2 -
div: Division of value
stack.1onstack.2
Data comparison
The cmp opcode is used to compare data on the stack. This opcode compares the top two elements of the stack and sets the value of the variable "code" to 0 if the values are the same, and to 1 if the values are different.
There are two opcodes for outputting data to the console:
-
out.0: Prints the value of
stack.1without a newline.call vm push "Message to output!" &:: Message to display on screen call vm out.0 &:: Printing the result written on the stack -
out.1: Prints the value
stack.1with a newline.call vm push "Message to output!" &:: Message to display on screen call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack
Other functions
The virtual machine also supports a number of other features:
-
cpuid: Returns information about the current processor in
stack.1. Preliminarily obtains the mode of data returned about the processor fromstack.1:- 1 - architecture
- 2 - identifier
- 3 - number of cores
- 4 - number of threads
- 5 - revision
call vm push 2 &:: Getting the processor ID call vm cpuid &:: Call cpuid call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
vcpuid: Returns information about the current virtual processor in
stack.1. Preliminarily obtains the mode of data returned about the processor fromstack.1:- 1 - version
- 2 - edition
call vm push 2 &:: Getting the virtual processor version call vm vcpuid &:: Call vcpuid call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
rand: Generates a random number in the range
0to32767and places it instack.1call vm push 0 &:: Stub value in stack.1 call vm rand &:: Getting a Random Number call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
nop (is reserved): An empty operation that does not perform any actions.
call vm nop &:: Doesn't do anything -
hw: Adds the string
Hello, world!to the stack. Doesn't have much practical application.call vm hw &:: Adds "Hello, world!" call vm out.1 &:: Printing the result written on the stack call vm clr &:: Clearing stack contents -
[unsafe]_$exec: Allows you to invoke shell commands (should be used with caution as it extends beyond the scope of the virtual machine).
-
[unsafe]_$exec_no_out: Performs the same functionality as
$exec, but blocks output to the console. -
[debug]_$stack: Prints the contents of all stack elements.
-
[debug]_$break: Pauses during program execution, waits for a key to be pressed.
Adviсe
- Don't forget to clean the stack with
clr - Comment your code
- Try to adhere to BatchASM standards
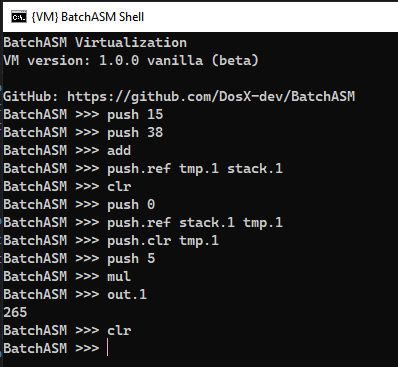
BatchASM Shell
You can try out BatchASM in command line mode using VM-SHELL.CMD
Calculation of mathematical expression (15 + 38) * 5
Thanks
- ShdBrk - helped port the original version of the documentation from HTML to MarkDown, translating it into English
- You - for your interest to this project!
❤️✨ Special thanks
- 👨🏼💻 @horsicq
